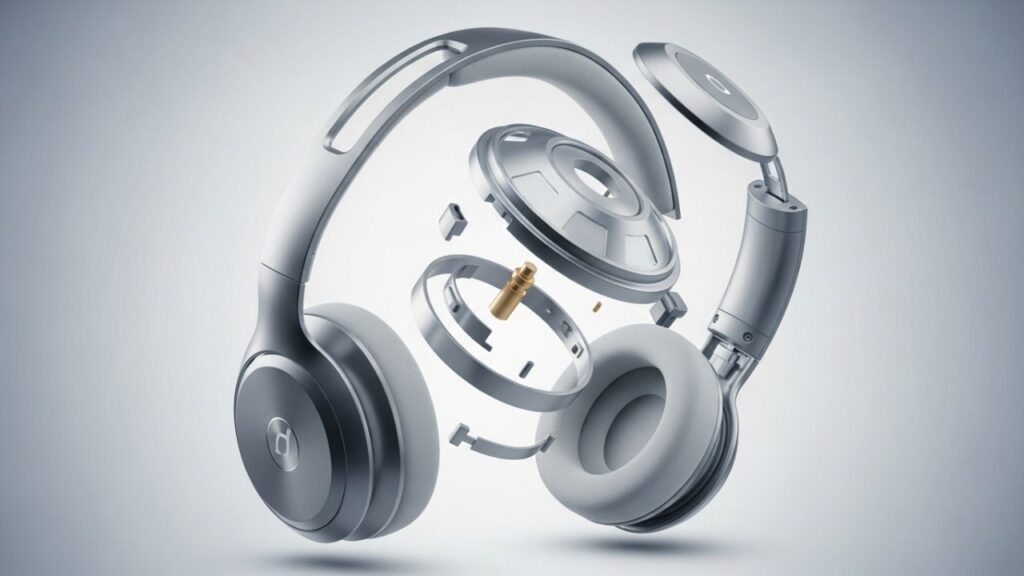
Introduction
Headphones have become a daily essential for millions of people—whether for music, gaming, work, or travel. But have you ever wondered how these tiny devices deliver such powerful sound? To understand their design and performance, you need to know the parts of headphones and how each component contributes to your listening experience.
In this article, we’ll explore the major parts of headphones, their functions, and why each one matters when choosing the right pair.
1. The Headband – The Backbone of Headphones
The headband is one of the most noticeable parts of headphones. It connects both earcups and helps the headphones rest comfortably on your head.
Functions of the Headband:
-
Support and Stability: Keeps the headphones in place, ensuring the earcups stay aligned with your ears.
-
Comfort Adjustment: Many headbands come with soft padding or memory foam to reduce pressure during long listening sessions.
-
Adjustability: Extendable sliders allow users to adjust the fit for different head sizes.
High-quality headbands are often made of metal, reinforced plastic, or flexible materials that combine strength with comfort.
2. Earcups – Where Sound Comes to Life
The earcups are the circular or oval structures that cover your ears. These are among the most vital parts of headphones since they house the main sound components.
Key Features of Earcups:
-
Enclosure Type: Earcups can be open-back or closed-back, affecting soundstage and noise isolation.
-
Material: Common materials include leather, synthetic leather, or breathable fabric, depending on whether comfort or durability is prioritized.
-
Design Influence: The earcup design greatly influences how immersive or natural the sound feels.
Closed-back earcups, for example, block outside noise and offer deep bass, while open-back models create a more spacious sound.
3. Ear Pads – Comfort Meets Acoustics
Ear pads (or cushions) are soft padding that surrounds the earcups. These are the parts of headphones that make direct contact with your skin, making comfort a key consideration.
Importance of Ear Pads:
-
Comfort: Good ear pads prevent pain and irritation during extended use.
-
Noise Isolation: The material and thickness affect how much external noise is blocked.
-
Sound Quality: Poorly fitted or worn ear pads can reduce sound clarity and bass response.
Premium headphones use memory foam or protein leather ear pads that mold to your ear shape, providing both comfort and superior sound insulation.
4. Drivers – The Heart of Every Headphone
When discussing the parts of headphones, the driver unit is the most crucial. It’s the component that converts electrical signals into audible sound waves.
Types of Drivers:
-
Dynamic Drivers: Most common; produce rich bass and powerful sound.
-
Balanced Armature Drivers: Found in high-end in-ear monitors for precise sound detail.
-
Planar Magnetic Drivers: Used in audiophile headphones for superior clarity and depth.
-
Electrostatic Drivers: Deliver unmatched accuracy but are more expensive and require an amplifier.
The size and quality of the driver directly influence how headphones perform in terms of volume, bass, and soundstage.
5. Speaker Diaphragm – The Sound Generator
Inside each driver is a diaphragm, a thin membrane that vibrates to produce sound. This is one of the most technical parts of headphones, but it’s also one of the most important.
Function of the Diaphragm:
When an audio signal passes through the driver coil, it creates a magnetic field that moves the diaphragm back and forth, producing sound waves that reach your ears.
Different materials (like mylar, graphene, or bio-cellulose) can dramatically affect tone, clarity, and durability.
6. Voice Coil – Powering the Sound
The voice coil works hand-in-hand with the magnet and diaphragm. It’s made of a thin copper or aluminum wire coiled around a lightweight frame.
Role of the Voice Coil:
-
Generates movement when electricity passes through it.
-
Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to move the diaphragm.
-
Directly impacts sensitivity and loudness.
This delicate component is one of the smallest yet most essential parts of headphones, responsible for transforming electrical impulses into physical sound.
7. Magnets – The Hidden Power Source
Every pair of headphones contains magnets that interact with the voice coil. Stronger magnets can create more precise sound reproduction.
Types of Magnets Used:
-
Neodymium: Lightweight, powerful, and energy efficient (most common today).
-
Ferrite: Heavier and less expensive but offers weaker magnetic fields.
These magnets form the core of the sound-producing mechanism in most modern headphone designs.
8. Cables and Connectors – The Bridge Between Device and Headphones
Even wireless headphones have internal cables and connectors linking the drivers to the main control board.
For Wired Headphones:
-
Audio Cable: Transfers audio signals from your device to the headphones.
-
Connectors: Common types include 3.5 mm jacks, 6.3 mm plugs, and USB-C connections.
-
Detachable Cables: Many premium models offer detachable cables for easier replacement.
For Wireless Headphones:
While wireless models rely on Bluetooth instead of physical cables, internal circuits and charging connectors still play similar roles.
9. Microphone and Control Buttons
In modern headphones—especially those for communication or gaming—microphones and control buttons are essential parts of headphones.
Functions:
-
Microphone: Enables calls, voice assistants, or in-game chat.
-
Control Buttons: Let users adjust volume, skip tracks, or answer calls without touching the connected device.
Some advanced headphones even include active noise-cancellation (ANC) buttons and touch controls for convenience.
10. The Circuit Board and Battery (Wireless Models)
For Bluetooth headphones, a circuit board acts as the control center. It manages sound processing, Bluetooth connectivity, and power management.
Key Elements:
-
Battery: Typically lithium-ion, powering wireless features for hours.
-
Bluetooth Chip: Manages pairing and signal transmission.
-
ANC Processor: Cancels external noise by generating counter-sound waves.
These high-tech components differentiate wireless headphones from their wired counterparts.
11. Housing and Frame – Protecting the Core
Finally, the housing and frame form the external shell that protects the internal parts of headphones from damage. It also influences acoustics, weight, and aesthetics.
High-end headphones often use metal, reinforced plastic, or carbon fiber, while budget models may opt for lightweight plastic to keep costs down.
Conclusion:
By knowing the parts of headphones, you gain a better appreciation of how these devices deliver such rich, detailed sound. Whether you’re an audiophile, gamer, or casual listener, understanding these components helps you make smarter purchasing decisions and maintain your headphones properly.
From the headband and earcups to the drivers and magnets, every part plays a specific role in sound reproduction and comfort. Next time you put on your headphones, you’ll know exactly how each piece contributes to your favorite tunes.